A priority queue is a commonly used abstract data type, but it is not adequately provided in Python’s standard library.
The module Queue provides a PriorityQueue class but that implementation leaves a lot to be desired.
It does not provide standard peek or remove methods in its public interface, which is sometimes critical.
Additionally, the entry must be in the tuple form (priority_number, data) where lower number must be used for higher priority task to be returned first.
Finally, this Queue version is reportedly slower because it adds locks and encapsulation designed for multi-threaded environment, which is arguably the intention of that module.
On the other hand, the module heapq provides an implementation of binary heap algorithms, which is the most common data structure for implementing priority-queue.
Although the module does not provide any direct implementation of priority-queue, its documentation discusses how to add additional capabilities to a heap-based priority queue and provides a recipe as an example.
That example is still hard to be used directly since it is not encapsulated into a class and the standard peek method is noticeably missing.
I ended up implementing a wrapper class for that recipe to make it easier to use.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 | |
Comparing to the recipe provided in heapq module, a few notes about this implementation:
- Task with higher priority goes out first. A simple change will remove lots of confusion (and bugs) associated with min-heap implementations.
- Methods and supporting data structures are encapsulated into a class.
- Method names are simplified to
add,remove,pop(instead ofadd_task, for example) since priority queues are NOT only used for task scheduling. - Method
peekis added. - Method
popandpeekreturn the highest-priority task together with its priority number. The task’s priority number can be useful sometimes (see Skyline problem below). - Override
__str__method for pretty printing.
As an example, the above priority-queue implementation is used to solve the Skyline problem. The Skyline problem states that:
You are given a set of n rectangular buildings on a skyline. Find the outline around that set of rectangles, which is the skyline when silhouetted at night.
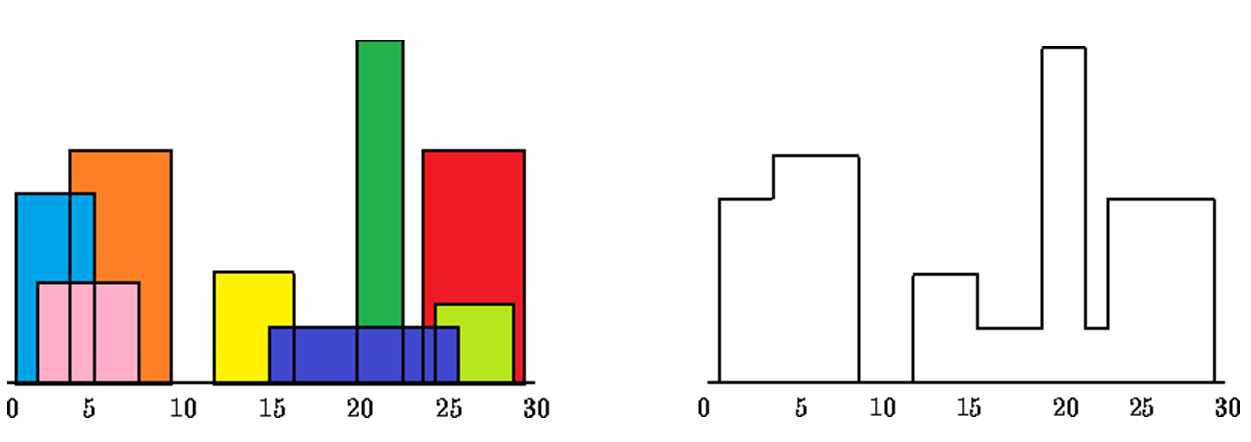
One possible approach is to use a priority queue to keep track of the current highest building while moving from left to right and adding/removing buildings at key points (i.e., start and end of buildings). Compared to the Merge-Sort-like approach detailed in this link, this approach is much more intuitive in my opinion while having similar runtime complexity $\mathcal{O}(n\log{}n)$.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 | |